The seminar was held as part of the project “Research dissemination” which is financially supported by the Minister of Science and Higher Education in Poland. The seminar’s aim was the presentation of research on work deroutinisation and the impact of globalisation and ICT technology on jobs demand and job quality in Europe, China and other emerging markets.
the effect of ICT, automation and offshoring on labour markets in emerging and middle-income countries
Technology and globalisation have changed the way work is performed around the world. Numerous studies showed that middle-skilled, routine-intensive employment is falling in the US and Western European countries, leading to job polarisation and driving up inequality. Automation, offshoring and import competition from emerging economies, especially China, are the commonly identified factors behind these changes. However, little attention has been given to the global picture and the effect of ICT, automation and offshoring on labour markets in emerging and middle-income countries. The studies presented at the seminar are parts of research conducted by:
- Institute for Structural Research (IBS)
- Institute for Emerging Market Studies, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)
- Institute of Population and Labor Economics, Chinese Academy of Social Science (CASS)
- Faculty of Management and Economics, Gdansk University of Technology (PG)



Albert Park (HKUST) showed the change of demand for specific job tasks in China, caused by four main factors: structural change, globalisation, technology and education. Du Yang (CASS) presented the results of the analysis of computer use by employees in China. He showed who (employee characteristics) and in which occupations uses computers the most, and if it is related to the levels of wages. Aleksandra Parteka (PG) discussed the preliminary results of her research, suggesting a strong correlation between the employee wages and the country’s involvement into global value chains.
task content of jobs
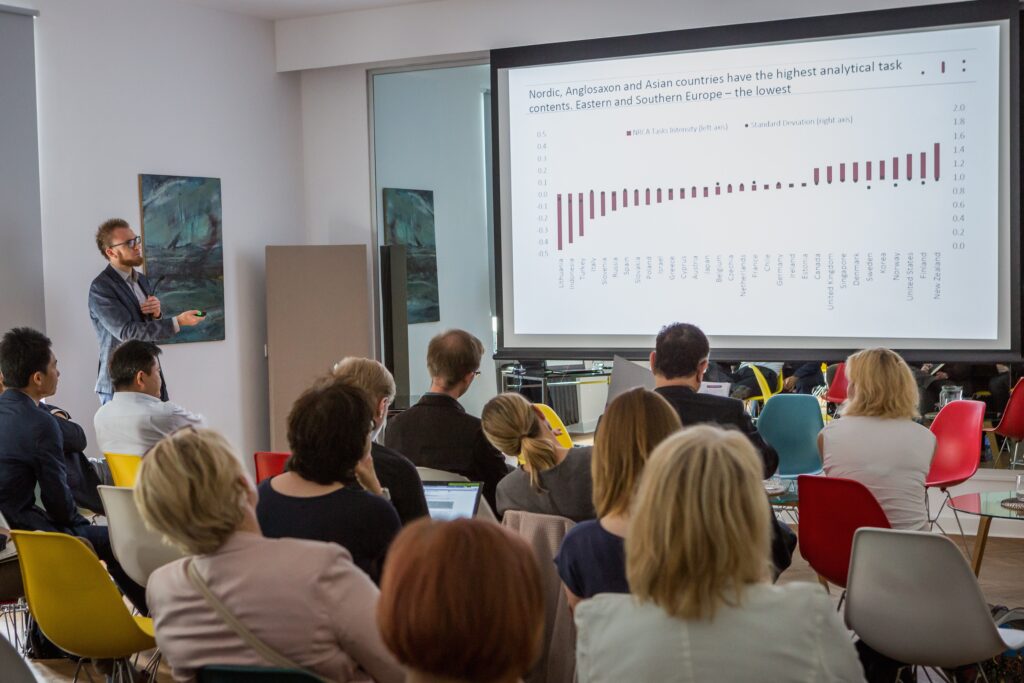
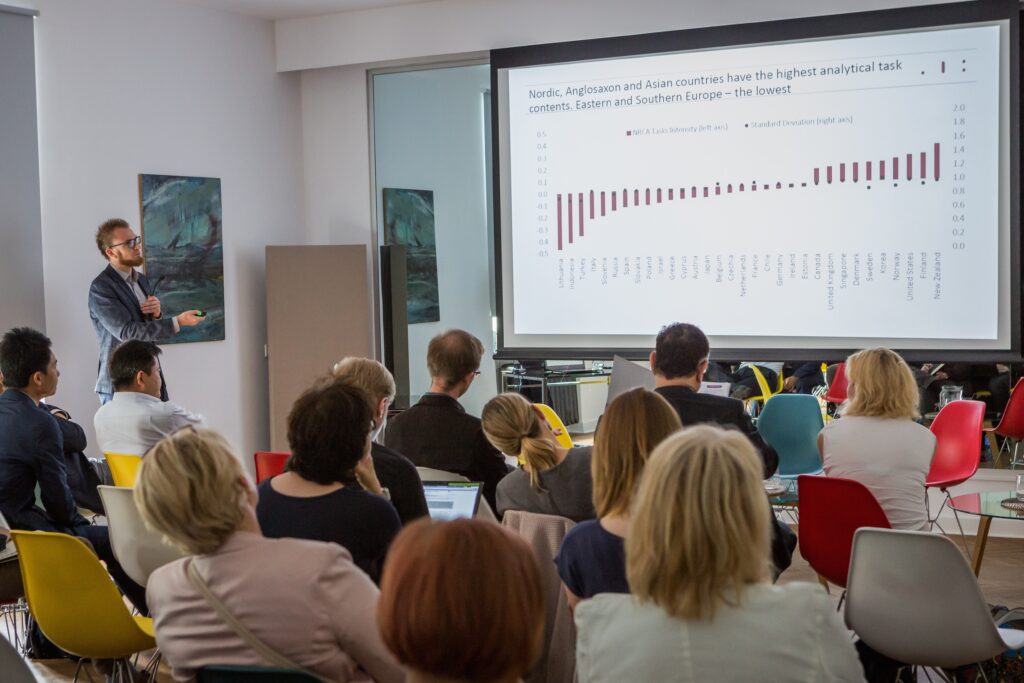
The Institute for Structural Research (IBS) was represented by Piotr Lewandowski, who showed the results of research, conducted together with Wojciech Hardy from IBS, on the global distribution of work in 40 countries around the world (including emerging markets). The IBS research contributes to current literature by means of the used measures. In literature the task content of jobs (their type and way of performing) is most often measured using the O*NET database on occupations in the US. Though this is a standard, it also eliminates any potential differences in occupations between countries. Some researchers construct measures based on individual data – STEP and PIAAC, but their comparability with O*NET data is limited. IBS researchers combine the O*NET comparability, while retaining the differences in occupations across countries, as evidenced in STEP and PIAAC data. The IBS analysis of the task intensities in 40 countries points to significant differences to the US not only in terms of the occupational structure, but also in terms of the tasks performed within each of the occupations.



The seminar was concluded with a panel discussion chaired by Krzysztof Kardaszewicz from the Centre of Migration Research (OBM). Piotr Lewandowski (IBS), Sławomir Majman (Dentons), Albert Park (HKUST) and Patrycja Pendrakowska (CSPA) discussed whether the Polish “reindustrialisation” plan is realistic in the light of automation and competition with Asia; whether the technological progress will change the prevailing patterns of global division of work around the world and how the Polish and Chinese labour markets will respond to the increasing levels of technology.
The “Technology, globalisation and the nature of work around the world” seminar was the first of a series of four international seminars (public policy seminars) organised by the Institute for Structural Research (IBS) in 2017. We encourage you to take part in the next seminar about economic inequalities in Poland, which will be held in Autumn.
text – bmk translation – am
The project is financially supported by the Minister of Science and Higher Education in Poland from resources for science dissemination (No. 892/P-DUN/2017).

- 9:00 – 9:30 Registration
- 9:30 – 9:40 IntroductionPiotr Lewandowski (Institute for Structural Research)
- 9:40 – 10:40 Session 1Globalisation and firm task demand: Evidence from China Albert Park (Hong Kong University of Science and Technology) Global value chains and wages Aleksandra Parteka (Gdansk University of Technology)
- 10:40 – 11:00 Coffee Break
- 11:00 – 12:00 Session 2Computer use at work and productivity improvement in China Yang Du (Chinese Academy of Social Science) The global distribution of routine and non-routine work – findings from PIAAC and STEP Piotr Lewandowski (Institute for Structural Research)
- 12:00 – 13:00 Panel discussionPiotr Lewandowski (Institute for Structural Research) Sławomir Majman (Dentons) Albert Park (Institute for Emerging Market Studies, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology) Patrycja Pendrakowska (Poland-Asia Research Center) Chair: Krzysztof Kardaszewicz (Centre of Migration Research)
- 12:50 – 13:00 SummaryPiotr Lewandowski (Institute for Structural Research)
 IBS_seminar_11.07.17_invitation.pdf
IBS_seminar_11.07.17_invitation.pdf
 IBS_seminar_11.07.2017_program.pdf
IBS_seminar_11.07.2017_program.pdf
 Albert_Park_Changing-Demand-for-Tasks-and-Skills-1.pdf
Albert_Park_Changing-Demand-for-Tasks-and-Skills-1.pdf
 Du_Yang_Computer-Use-and-Productivity-1.pdf
Du_Yang_Computer-Use-and-Productivity-1.pdf
 Piotr_Lewandowski_Global_distribution_of_non-routine_work_070717-1.pdf
Piotr_Lewandowski_Global_distribution_of_non-routine_work_070717-1.pdf


